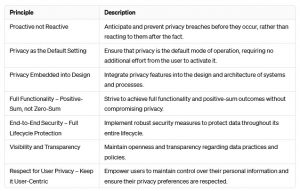
| Start Early and Involve Stakeholders | Incorporate privacy considerations from the outset of any project or product development. Engage stakeholders, including developers, designers, and legal experts, to ensure a holistic approach to privacy. | – Ensures that privacy considerations are integrated into the project from the beginning, reducing the need for costly retrofits.<br>- Improves collaboration and understanding across different teams, leading to more effective privacy solutions.<br>- Minimizes the risk of overlooking privacy requirements, thus avoiding potential legal and reputational consequences. |
| | | |
| Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation | Collect only the data that is necessary for specified, explicit, and legitimate purposes. Minimize data collection and processing activities to reduce the risk of privacy breaches. | – Reduces the amount of data stored, lowering storage and processing costs.<br>- Decreases the risk of data breaches by limiting the volume of sensitive information.<br>- Enhances trust and loyalty among customers by demonstrating respect for their privacy and minimizing intrusive data collection. |
| | | |
| User Consent and Control Mechanisms | Implement robust mechanisms for obtaining informed and explicit consent from users before collecting their personal data. Provide users with granular control over their data, including the ability to access, edit, or delete it. | – Builds trust with users by providing them with transparency and control over their personal data.<br>- Helps businesses comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.<br>- Increases user engagement and satisfaction by allowing them to tailor their privacy preferences according to their preferences. |
| | | |
| Security by Design and Default | Integrate security measures into the design and architecture of systems and processes. Implement encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. | – Mitigates the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks, safeguarding sensitive information.<br>- Enhances the organization’s reputation for reliability and trustworthiness among customers and partners.<br>- Reduces the likelihood of legal liabilities and financial losses associated with data breaches. |
| | | |
| Transparency and Accountability | Be transparent about data practices and policies. Provide clear and easily accessible information to users about how their data is collected, processed, and used. Establish accountability mechanisms within the organization to ensure compliance with privacy regulations. | – Fosters trust and loyalty among users by being open and honest about data practices.<br>- Helps businesses maintain compliance with privacy regulations, avoiding costly legal consequences.<br>- Enhances brand reputation and differentiation in the market as a privacy-conscious organization. |
| | | |
| Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) | Conduct Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) to identify and mitigate privacy risks associated with new projects, products, or initiatives. PIAs help organizations assess the impact of their activities on individual privacy rights and take appropriate measures to address any identified risks. | – Identifies potential privacy risks early in the development process, allowing for proactive mitigation measures.<br>- Demonstrates commitment to privacy compliance, which can strengthen relationships with partners and customers.<br>- Helps organizations avoid costly data breaches and regulatory fines by addressing privacy concerns before they escalate. |
| | | |
| Employee Training and Awareness | Educate employees about the importance of privacy and their role in protecting personal data. Provide regular training sessions and awareness programs to foster a privacy-conscious culture within the organization. | – Empowers employees to recognize and respond to privacy risks effectively, reducing the likelihood of data mishandling incidents.<br>- Cultivates a privacy-aware culture within the organization, encouraging responsible data handling practices.<br>- Enhances overall data security posture by ensuring that employees understand their role in protecting sensitive information. |
| | | |
| Continuous Monitoring and Improvement | Implement processes for continuous monitoring and improvement of privacy practices. Regularly review and update privacy policies, procedures, and technologies to adapt to changing regulatory requirements and emerging privacy risks. | – Enables organizations to stay ahead of evolving privacy threats and regulatory requirements.<br>- Demonstrates commitment to ongoing compliance and risk management, enhancing trust with stakeholders.<br>- Allows for timely adjustments to privacy practices, technologies, and policies in response to emerging threats or changes in business operations. |